Why Compliance Matters in Plastic Packaging
Plastic is the backbone of modern packaging. From grocery bags and shipping films to medical gloves and food containers, it protects products, extends shelf life, and supports global trade.
But with increasing awareness of sustainability, governments are enforcing stricter packaging laws. Businesses that don’t understand plastic packaging compliance risk fines, shipment delays, or outright bans in key markets.
For U.S. retailers, wholesalers, and distributors, this means one thing: compliance is no longer just a legal requirement — it’s a competitive advantage.
At TP Plastic USA, we’ve helped businesses navigate FDA, EU, and Asia-Pacific standards for decades. This guide breaks down everything you need to know to stay compliant and succeed in global trade.
What Is Plastic Packaging Compliance?
Plastic packaging compliance refers to a set of rules, certifications, and standards that packaging must meet before being sold or exported. These cover:
-
Material safety – ensuring plastics used for food contact are non-toxic and approved.
-
Labeling & traceability – resin codes, recycling instructions, warnings.
-
Sustainability obligations – restrictions on single-use plastics, recycling targets, biodegradability.
-
Import/export approvals – documents and test reports required at customs.
In short: compliance ensures safety, sustainability, and legality across every market you sell to.
U.S. Regulations: FDA, ASTM, and State Laws
1. FDA Regulations for Food Contact Plastics
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates packaging that touches food under Title 21 CFR.
Approved materials for common use include:
-
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene): Grocery bags, milk jugs.
-
LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene): Wraps, liners, trash bags.
-
PP (Polypropylene): Microwave-safe containers, bottle caps.
Packaging must pass migration tests to ensure chemicals don’t leach into food.
2. ASTM Standards
The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) provides voluntary but widely recognized standards such as:
-
ASTM D6400: Compostable plastics certification.
-
ASTM D883: Standard terminology for plastics.
-
ASTM D3985: Oxygen transmission rate testing (important for food).
Many buyers, especially in retail and food service, demand ASTM-certified plastics.
3. State-Level Bag Regulations
States like California, New York, and Oregon have bans or restrictions on single-use plastic bags. Compliance may require:
-
Minimum thickness (e.g., 2.25 mils for reusable bags in California).
-
Mandatory recycled content percentages.
-
Bag fees or labeling requirements.
For U.S. wholesalers, this means tailoring packaging by state-specific rules.
European Union Regulations: The Strictest Standards
1. EU Framework and Food Safety
All plastics must comply with Framework Regulation (EC) No. 1935/2004. Food contact plastics must also meet EU Regulation 10/2011, which lists authorized materials and maximum migration levels.
2. The Single-Use Plastics Directive (SUPD)
Since 2021, the EU has banned certain plastic products (like straws, polystyrene foam containers, and some carrier bags). For remaining plastics, strict labeling rules apply.
3. Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
Producers must pay fees to recycling systems. Non-compliance can lead to your products being delisted by retailers like Carrefour, Tesco, or Aldi, all of which enforce strict sustainability policies.
Asia-Pacific: Rapidly Changing Rules
1. Japan
-
Packaging must meet the Food Sanitation Act.
-
Importers often require detailed documentation and migration test results.
2. China
-
National ban on ultra-thin bags (<25 microns).
-
Many provinces mandate biodegradable alternatives.
3. South Korea & Taiwan
-
Require recycling labels on all plastic packaging.
-
Promote waste reduction via consumer-facing deposit systems.
4. Australia
-
Phasing out single-use plastics by 2025 under the National Packaging Targets.
The Role of Resin Selection in Plastic Packaging Compliance
The base plastic resin often determines whether your packaging is compliant.
-
HDPE (2): Strong, recyclable, widely accepted.
-
LDPE (4): Flexible, safe for food, recyclable in store drop-offs.
-
PP (5): High heat resistance, safe for food contact.
-
PVC (3): Increasingly banned/restricted in many markets.
-
PLA (7): Compostable, requires certification to be accepted.
At TP Plastic USA, we focus on resins that balance performance, cost, and compliance.
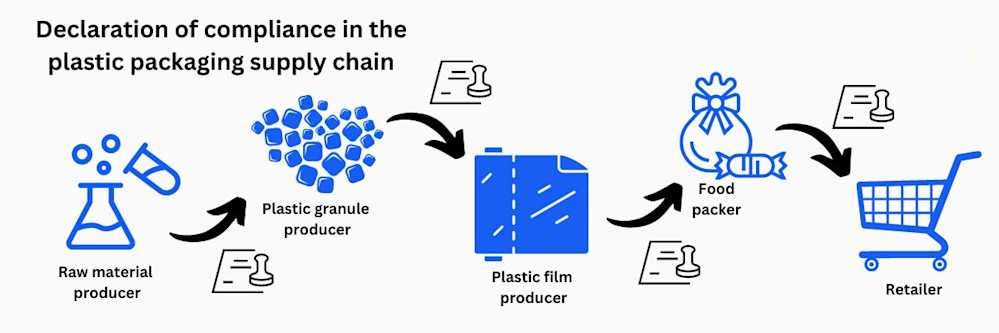
Documentation You May Need for Exports
When exporting, customs authorities or buyers may request:
-
FDA compliance letter (U.S. food packaging).
-
Declaration of Compliance (DoC) (EU food contact plastics).
-
Migration test reports (Japan, EU).
-
Compostability certificates (ASTM D6400, EN13432).
-
Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS).
Having these documents ready ensures smoother trade.
Case Studies: Real-World Plastic Packaging Compliance Challenges
Case 1: U.S. Distributor to Germany
A U.S. distributor of frozen foods was blocked at German customs for not having an EU Declaration of Compliance. Switching to HDPE bags with certified testing from TP Plastic USA solved the issue, unlocking sales across the EU.
Case 2: Retail Chain in California
A national grocery chain faced fines because its bags didn’t meet California’s minimum thickness law. With TP Plastic’s 2.25-mil compliant reusable bags, they avoided penalties and gained eco-friendly branding.
Practical Tips for Businesses
-
Check destination market rules before selecting packaging.
-
Use certified suppliers who provide documentation.
-
Avoid PVC and restricted plastics when exporting.
-
Leverage OEM/ODM for custom compliance solutions.
-
Educate your customers — compliance labeling boosts trust.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Does the recycling triangle symbol guarantee recyclability?
No. It indicates resin type, not whether your local facility accepts it.
Q2: Can I export non-compliant packaging if my buyer doesn’t care?
No. Customs authorities enforce regulations regardless of buyer preference.
Q3: Are biodegradable plastics always compliant?
Only if certified under recognized standards (e.g., ASTM D6400, EN13432).
Q4: Do I need separate packaging for U.S., EU, and Japan?
Often yes, but with smart OEM/ODM design, one packaging line can meet multiple standards.
How TP Plastic USA Supports Plastic Packaging Compliance
We don’t just supply bags and films — we provide compliance assurance.
-
FDA & EU-approved resins (HDPE, LDPE, PP).
-
OEM/ODM customization with logos and labeling.
-
Documentation support for export markets.
-
Sustainable options (compostable, recycled content).
Conclusion: Compliance Is a Growth Opportunity
Plastic packaging compliance may seem complex, but it is the gateway to global trade. Businesses that embrace compliance not only avoid risks but also:
-
Win consumer trust.
-
Access new markets.
-
Future-proof their supply chains.
At TP Plastic USA, we combine quality materials, global certifications, and compliance expertise to help your business grow.
TP Plastic USA – The quality you can trust!
Zalo/WhatsApp: (+1) 818 914 – 0351
Website: tpplasticusa.com
Email: contact@tpplasticusa.com