Why Plastic Resin Codes Matter
Every plastic product you encounter — from grocery bags to beverage bottles — is made from a specific type of polymer. Each of these polymers behaves differently in terms of durability, flexibility, chemical resistance, and recyclability.
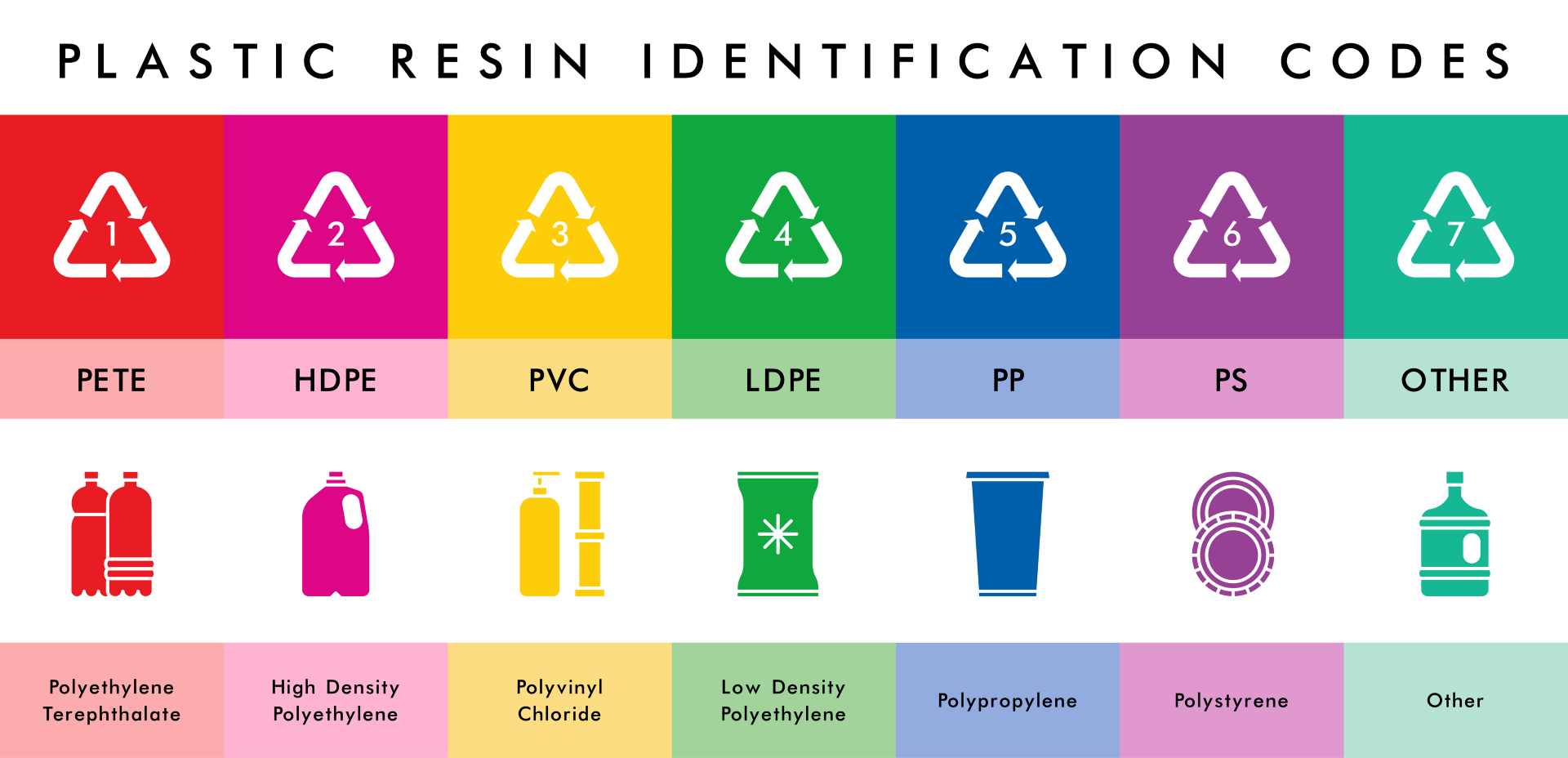
The plastic resin code, also called a Resin Identification Code (RIC), is a simple way to communicate this material information. It’s a small number inside a recycling triangle, usually molded into the bottom or side of the product.
While many consumers assume these numbers indicate recyclability, in reality they identify the type of plastic resin used — and whether or not it can be recycled depends heavily on local recycling capabilities.
For retailers, wholesalers, and manufacturers, understanding these codes is important for:
-
Selecting the right material for product performance
-
Ensuring compliance with food safety and environmental regulations
-
Providing accurate product information to customers
-
Supporting sustainability and recycling efforts
At TP Plastic USA, we work with multiple plastic resin types to produce a wide range of packaging products, including bags, gloves, aprons, stretch films, and protective mailers.
What Are Plastic Resin Codes?
Plastic resin codes were introduced in 1988 by the Society of the Plastics Industry (now known as the Plastics Industry Association). The goal was to make it easier for recycling facilities to sort plastics by type, since each resin must be processed separately.
The codes are numbered 1 through 7 and are universally recognized in packaging and manufacturing. The number identifies the polymer, while the triangular arrows are a nod to recycling, though resin code ≠ recyclable in all areas.
The 7 Plastic Resin Codes Explained in Detail
1 – PET or PETE (Polyethylene Terephthalate)
-
Properties: Clear, lightweight, strong, impact-resistant.
-
Common Uses: Soda and water bottles, salad dressing containers, peanut butter jars.
-
Recyclability: Widely accepted; can be turned into polyester fiber for clothing, carpets, and reusable bottles.
-
Business Tip: PET is ideal for products requiring clarity and food safety.
2 – HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene)
-
Properties: Strong, opaque, resistant to moisture and chemicals.
-
Common Uses: Milk jugs, detergent bottles, grocery bags, drawstring trash bags.
-
Recyclability: Widely accepted; can be recycled into piping, plastic lumber, and new containers.
-
Example at TP Plastic USA: Grocery/T-shirt bags and heavy-duty trash bags.
3 – PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
-
Properties: Rigid or flexible, chemical-resistant, long-lasting.
-
Common Uses: Plumbing pipes, vinyl siding, clear food packaging.
-
Recyclability: Limited; difficult to process due to chlorine content.
-
Note: TP Plastic USA focuses on PE and PP rather than PVC for packaging, as it’s less recycling-friendly.
4 – LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene)
-
Properties: Flexible, transparent, moisture-resistant.
-
Common Uses: Bread bags, shrink wrap, PE stretch film, produce bags.
-
Recyclability: Accepted in some store drop-off programs; can be made into garbage can liners, floor tiles.
-
Example at TP Plastic USA: Stretch films for shipping, LDPE produce bags.
5 – PP (Polypropylene)
-
Properties: High melting point, chemical resistance, durability.
-
Common Uses: Yogurt containers, caps, reusable food storage.
-
Recyclability: Growing acceptance; used to make signal lights, battery cables, brooms.
-
Example: Specialty packaging films.
6 – PS (Polystyrene)
-
Properties: Lightweight, rigid, insulating.
-
Common Uses: Disposable plates, foam cups, packing peanuts.
-
Recyclability: Limited; often ends up in landfills.
7 – Other (Including PLA, Polycarbonate, Multi-layer Plastics)
-
Properties: Varies; can include bio-based and high-performance plastics.
-
Common Uses: Multi-layer pouches, reusable water bottles, compostable bags (PLA).
-
Recyclability: Dependent on specific polymer type and local facilities.
Why Plastic Resin Codes Are Important for Businesses
Plastic resin codes are not just for recycling plants — they’re a quality control and compliance tool. Businesses use them to:
-
Avoid material mismatch – Using the wrong resin for a product’s function can lead to failures.
-
Meet food-contact regulations – Certain resins like PET and HDPE are FDA-approved for food use.
-
Plan for sustainability goals – Choosing recyclable resins supports brand responsibility.
-
Communicate with buyers – Especially important for B2B clients who require material transparency.
How TP Plastic USA Incorporates Resin Codes into Production
We primarily work with:
-
HDPE (2) for grocery and T-shirt bags, drawstring trash bags
-
LDPE (4) for stretch films, produce bags
-
PP (5) for specialty packaging
Example: Our PE stretch film (LDPE) is engineered for high cling and load stability, making it ideal for shipping and warehousing. All our products are labeled with the correct resin code to ensure transparency and simplify disposal.
Compliance and Global Standards
Many regions now have Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) laws that require accurate labeling of plastic products. Incorrect or missing resin codes can result in penalties.
In the United States, resin code use is guided by ASTM D7611 standards.
In the European Union, packaging materials must also meet labeling regulations to comply with Directive 94/62/EC.
In Canada and Australia, resin codes help meet waste reduction targets under national packaging agreements.
Tips for Choosing the Right Plastic Resin for Your Needs
-
Match resin to application: HDPE for strength, LDPE for flexibility, PET for clarity.
-
Factor in local recycling access: If your target market has limited recycling, consider reusable or compostable options.
-
Balance cost and performance: Higher-performance resins may cost more but last longer.
-
Consider branding: Some customers prefer eco-friendly materials for marketing appeal.
Sustainability and the Future of Resin Codes
With increasing environmental awareness, the role of resin codes is evolving. The packaging industry is seeing:
-
Growth in bio-based resins like PLA (code 7)
-
Demand for single-polymer packaging to simplify recycling
-
Stricter eco-labeling laws in many markets
At TP Plastic USA, we are actively exploring compostable options and recycled resin integration to meet future demand.
Conclusion
Understanding plastic resin codes gives you the power to make smarter, more sustainable packaging choices. Whether you’re in retail, wholesale, or manufacturing, knowing your materials means better performance, compliance, and customer trust.
TP Plastic USA supplies products made from carefully selected resins to meet your needs — from HDPE trash bags to LDPE stretch film — all clearly labeled for transparency.
TP Plastic – The quality you can trust
Zalo/WhatsApp: (+84) 915 871 722 / (+1) 818 914 – 0351
Website: tpplasticusa.com
Email: contact@tpplasticusa.com